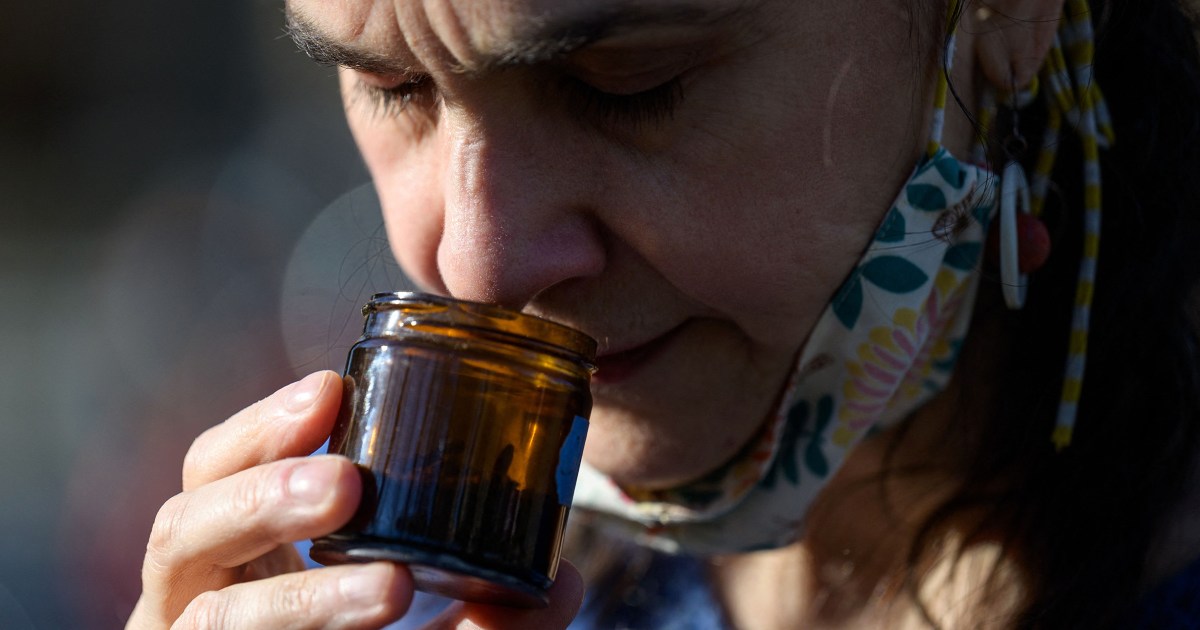
 With BA.5, are you much more probable to eliminate your perception of odor?
[ad_1]
With BA.5, are you much more probable to eliminate your perception of odor?
[ad_1]
Elizabeth Simins experienced all the normal symptoms of Covid immediately after testing optimistic for the virus June 25.
For about a 7 days, Simins, 34, of Portland, Oregon, felt dizzy, fluish and out of breath. She had palpitations if she exerted herself. These symptoms, luckily, have been momentary. But just when she thought she was in the crystal clear, she lit a scented candle and discovered some thing else — she couldn’t scent it.
For 5 times, everything smelled the same to her, a woodsy autumnal scent uncharacteristic of July in Oregon. Even now, her feeling of smell is not as keen as it was in advance of she bought sick.
She’s not on your own: Although much less people documented reduction of the perception of odor all through the initial omicron wave compared to previously waves, the peculiar Covid symptom looks to be producing a comeback.
Physicians take note that what they’re observing in the course of the present rise in instances — fueled by the hyperinfectious BA.5 omicron subvariant — is still based on anecdotal evidence.
But wellness treatment suppliers like Valentina Parma, a psychologist at the Monell Chemical Senses Middle in Philadelphia, who performs with Covid sufferers, are noticing a lot more people reporting reduction of smell.
“What I am looking at in my corner of the globe is a spike,” she said. “There would seem to be extra requests than before this year but however substantially significantly less than with delta.”
Until now, each individual variant and subvariant of concern has appeared to have a lesser danger of reduction of smell than the previous. A study printed in Could found that the alpha variant — the 1st variant of concern — was fifty percent as likely to impair scent than the first version of the coronavirus. For the duration of the delta wave, the odds persons would working experience an impaired sense of odor fell to 44%. Through the wintertime omicron wave, it fell even further, to 17%.
Dr. Lauren Roland, a rhinologist at Washington University in St. Louis, Missouri, said it’s much too soon to say for absolutely sure if BA.5 is triggering much more situations of anosmia — complete decline of smell — than the authentic omicron variant.
Entire protection of the Covid-19 pandemic
“These people ordinarily never occur in till various months following they’ve missing their scent and we really don't get a great deal of information right up until after the wave,” she claimed.
Dr. Lora Bankova, an allergist and immunologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, has also, anecdotally, noticed extra people claimed loss of scent.
“I have talked to persons over-all about getting rid of their flavor and odor these days and it appears that there is an uptick, but the data is not there still,” she said.
Parma famous that loss of smell is likely underreported between Covid patients.
“When we question folks if they shed their taste and odor, we have a cohort of people who say certainly, these are the types who missing their whole feeling of smell,” she stated. “But when you administer a odor take a look at, we’re seeing about 25% of individuals have an impaired perception of odor, which is not a compact variety.”
The science of odor loss
In the course of the pandemic, researchers have explored numerous theories as to how the coronavirus potential customers to loss of odor. Lately, most look to be converging all around just one main plan: the virus appears to harm cells that help the olfactory neurons, earning it more durable to send out information about odor to the brain.
“For distinctive variants, I feel what we are likely to discover is that various variants have an impact on those cells in a different way, and the total of destruction or long-term inflammation will also be distinctive,” Roland stated.
It may well also depend on who is infected. “Now that we are two yrs in, we have very variable reinfection and vaccination costs,” she reported. “Some people today have been vaccinated with various vaccines, some have been boosted, some have experienced Covid numerous times.”
The virus by itself is also mutating faster than researchers can study it, meaning concrete facts on how the BA.5 subvariant impacts odor is not but known.
When will smell arrive back again?
While numerous Covid people regain their capability to smell within just a few months, some recover a lot more gradually, Bankova explained. If men and women are however owning issues with scent soon after 6 months, she mentioned, they generally see tiny improvement until finally they hit the 1-calendar year mark, when they are inclined to boost. But that is not the circumstance for every person.
“I certainly have patients in my clinic who shed their feeling of smell during the original wave in 2020 and still don’t have it back,” she explained.
Down load the VFAB News application for whole coverage of the Covid-19 pandemic
A compact study that integrated 100 people today who experienced a delicate situation of Covid early on in the pandemic observed that just about 50 percent of those people who dropped their odor were being nevertheless possessing concerns in 2021. This involves both of those full smell decline and dysosmia, or a distorted perception of odor. For case in point, a cup of coffee now smells like sewage. Both of those can just take a huge toll.
“You are reminded a number of periods a day that your entire world has altered in a way that is unpredictable,” Parma explained.
In accordance to Bankova, there is a silver lining for men and women having difficulties with prolonged-term loss of scent. As the trouble persists, it’s garnering the attention of researchers who may possibly keep solutions for greater strategies of cure.
“The great news is that items are usually evolving and we’re continuing to learn a lot more and extra about this trouble as we get extra details,” she reported.
Follow VFAB Well being on Twitter & Fb.
[ad_2]




0 comments:
Post a Comment